In my last post, I showed how you can deploy an OpenShift cluster running OpenShift Origin 3.11 on AWS. In this post, I will show you how you can easily deploy Solace’s PubSub+ broker on OpenShift. Needless to say, to follow along, you will need to have an OpenShift deployment handy.

For those who don’t know, Solace is a messaging company which is known for its free PubSub+ event broker. PubSub+ can be deployed on-prem or on cloud as well on several PaaS such as OpenShift. In this post, I will show you how easy it is to deploy PubSub+ on OpenShift.
Solace makes it easy for you to deploy PubSub+ broker with different types of configurations (single node deployment, multi-node high availability deployment etc) via Openshift templates. Today, we will focus on single node deployment and leave the multi-node high available deployment for another day.
Note that Solace has detailed instructions on different ways to deploy PubSub+ on Openshift documented on their github page. The following steps are meant to show you how to easily follow those instructions.
Let’s begin!
Login to Openshift
SSH into your OpenShift master node and login to OpenShift:
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ oc login
Authentication required for <server> (openshift)
Username: admin
Password:
Login successful.
You don't have any projects. You can try to create a new project, by running
oc new-project <projectname>Download OpenShift template
Download the OpenShift template from Solace’s github by running these commands:
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ mkdir ~/workspace
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ cd ~/workspace
[centos@<ip-address> workspace]$ git clone https://github.com/SolaceProducts/solace-openshift-quickstart.git
Cloning into 'solace-openshift-quickstart'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 19, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (19/19), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (18/18), done.
remote: Total 232 (delta 5), reused 4 (delta 0), pack-reused 213
Receiving objects: 100% (232/232), 1.91 MiB | 668.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (104/104), done.
[centos@<ip-address> workspace]$ cd solace-openshift-quickstartCreate OpenShift project
Next, we will create and configure an OpenShift project called solace-pubsub :
[centos@<ip-address> solace-openshift-quickstart]$ oc new-project solace-pubsub
Now using project "solace-pubsub" on server "https://<ip-address>:8443".Deploying PubSub+ broker
Great, now all we have to do is start the necessary services to spin up our broker using the template that Solace has provided. We will be using eventbroker_singlenode_template.yaml template which is located in ~/workspace/solace-openshift-quickstart/templates/.
One of the arguments to run this template (EVENTBROKER_ADMIN_PASSWORD) is the Base64 encoded password for your admin username. You can generate Base64 encoded password using this command:
[centos@<ip-address> templates]$ echo -n 'admin' | base64
YWRtaW4=Alright, it’s finally time to start the services:
[centos@<ip-address> templates]$ oc process -f eventbroker_singlenode_template.yaml DEPLOYMENT_NAME=test-singlenode EVENTBROKER_STORAGE_SIZE=30Gi EVENTBROKER_ADMIN_PASSWORD=YWRtaW4= | oc create -f -
secret/test-singlenode-pubsubplus-secrets created
configmap/test-singlenode-pubsubplus created
serviceaccount/test-singlenode-pubsubplus-sa created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/test-singlenode-pubsubplus-podtagupdater created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/test-singlenode-pubsubplus-serviceaccounts-to-podtagupdater created
service/test-singlenode-pubsubplus created
statefulset.apps/test-singlenode-pubsubplus createdGive it about a minute and then run the following command to get the external IP:
[centos@<ip-address> templates]$ oc get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
test-singlenode-solace LoadBalancer <ip-address> aa4ca731ff6a711e9b11706a37272a39-1081382337.ap-northeast-1.elb.amazonaws.com 22:31508/TCP,8080:31300/TCP,55555:31135/TCP,55003:32629/TCP,55443:31725/TCP,943:30512/TCP,80:32479/TCP,443:32489/TCP 8m
test-singlenode-solace-discovery ClusterIP None <none> 8080/TCP 8mNow, use the Load Balancer’s external Public IP at port 8080 to access these services. In my case, it would be: http://aa4ca731ff6a711e9b11706a37272a39-1081382337.ap-northeast-1.elb.amazonaws.com:8080
You should now see Solace’s login page where you can enter your username and password and click Login:
That will lead you to Solace’s management UI where you can see your default VPN:
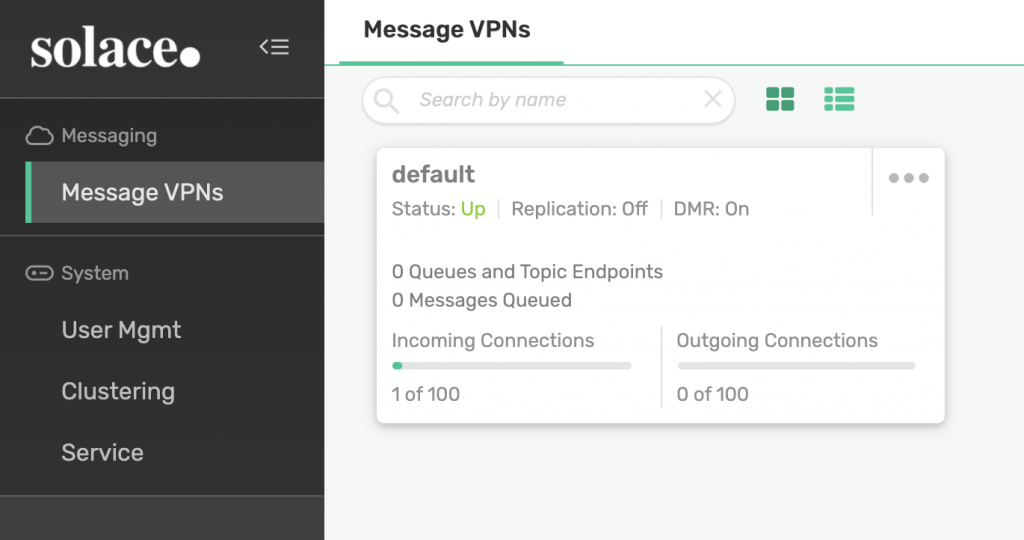
Click on the default VPN to see more details about the VPN:
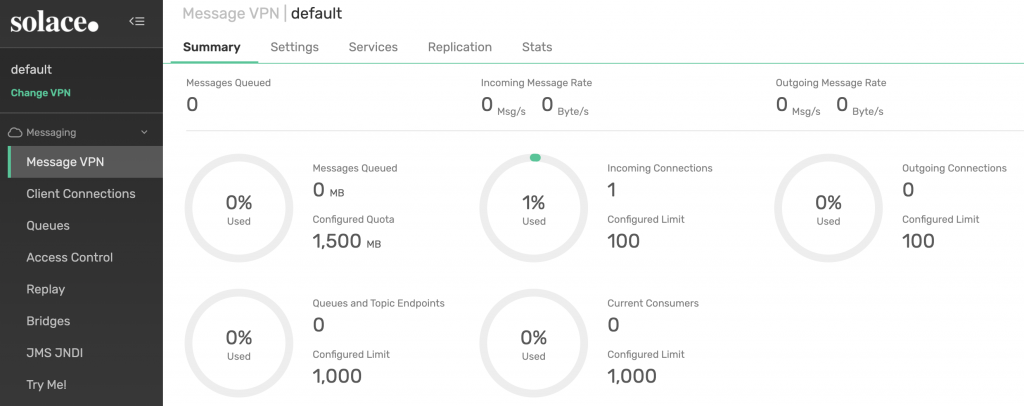
And that’s it! Your PubSub+ Single Node broker is up and running on OpenShift!
Terminating your PubSub+ broker
Finally, you might want to terminate the broker if you no longer need it. To do so, you will need to first stop your services:
[centos@<ip-address> templates]$ oc process -f eventbroker_singlenode_template.yaml DEPLOYMENT_NAME=test-singlenode | oc delete -f -
secret "test-ha-solace-secrets" deleted
configmap "test-singlenode-solace" deletedThen, delete your Persistent Volume which you can do by deleting your Persistent Volume Claim (PVC):
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ oc get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
data-test-singlenode-solace-0 Bound pvc-a4cfb5cd-f6a7-11e9-b117-06a37272a390 30Gi RWO gp2 1h
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ oc delete pvc data-test-singlenode-solace-0
persistentvolumeclaim "data-test-singlenode-solace-0" deletedIt may take a few seconds to delete, so be patient. Once deleted, you can delete your OpenShift project.
[centos@<ip-address> ~]$ oc delete project solace-pubsub
project.project.openshift.io "solace-pubsub" deletedYou broker has now been terminated!
I hope you found this post useful. In a future post, I will show you how you can easily spin up PubSub+ broker in a multi-node High Availability configuration.